Science
Scientists Unravel Mystery Behind Blinding Blue Flashes in Space
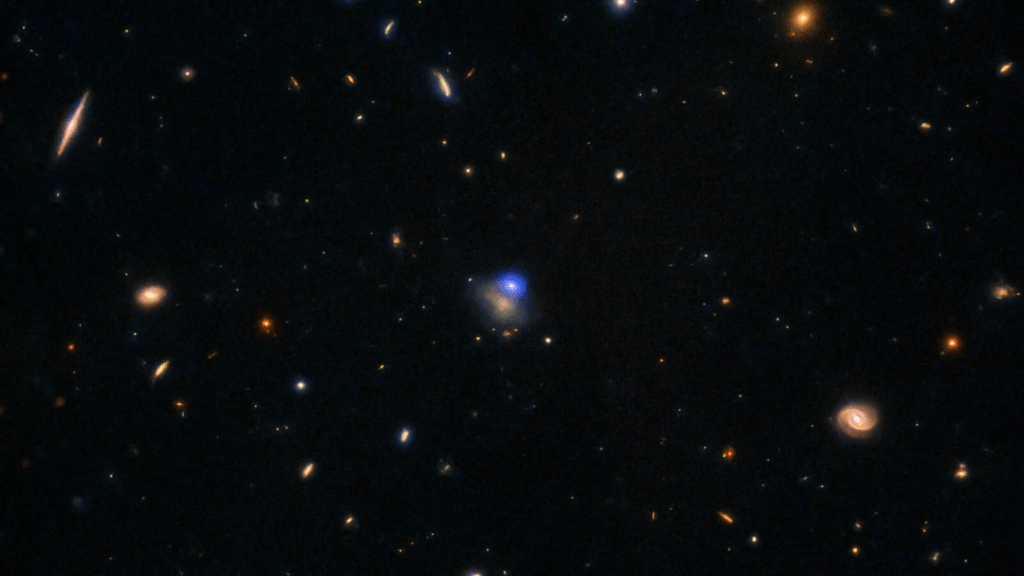
Astronomers have made significant strides in understanding the phenomenon known as luminous fast blue optical transients (LFBOTs), which appear as blinding blue flashes in the cosmos. These events are remarkable, as they can outshine entire galaxies for a few days before fading into faint emissions of X-rays and radio waves. Until recently, the origin of these mysterious flashes remained elusive.
Recent research, published in two separate papers on arXiv, has shed light on one such event designated as AT 2024wpp. Observations indicate that this particular LFBOT is approximately 100 times brighter than a typical supernova, suggesting that it is not a conventional stellar explosion. The immense brightness of AT 2024wpp implies that a star would have to convert an extraordinary portion of its mass into energy to reach such luminosity. While black holes can achieve this, AT 2024wpp does not appear to be a black hole itself, raising questions about its actual cause.
According to scientists, AT 2024wpp is likely the result of a relatively small black hole, estimated to be no more than 100 times the mass of the Sun, consuming a companion star. As the black hole tore apart the star, the material was drawn into an accretion disk, generating intense ultraviolet, X-ray, and blue light. Some of this material was then expelled in jets moving at nearly the speed of light, creating the radio waves that astronomers detect after the initial flash subsides.
Exploring the Implications of LFBOTs
The discovery of LFBOTs like AT 2024wpp provides astronomers with a novel opportunity to study medium-sized black holes. By identifying the locations of these flashes within galaxies, researchers aim to gain insights into the formation of black hole-star pairings. This research could ultimately enhance our understanding of the dynamics within galaxies and the evolution of such celestial systems.
The study of LFBOTs represents a significant breakthrough in astrophysics, as it opens new avenues for exploring the complexities of black holes and their interactions with surrounding stars. With each flash offering a unique glimpse into the universe’s workings, astronomers are eager to continue their investigations into these extraordinary cosmic events.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
 Science1 month ago
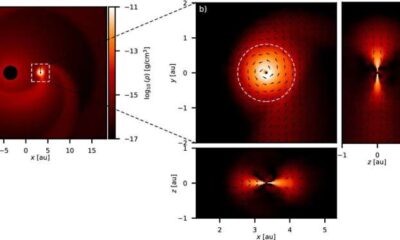
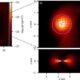
Science1 month agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws








