Science
Mars Dust Storms Generate Electric Sparks, Revealing New Chemistry
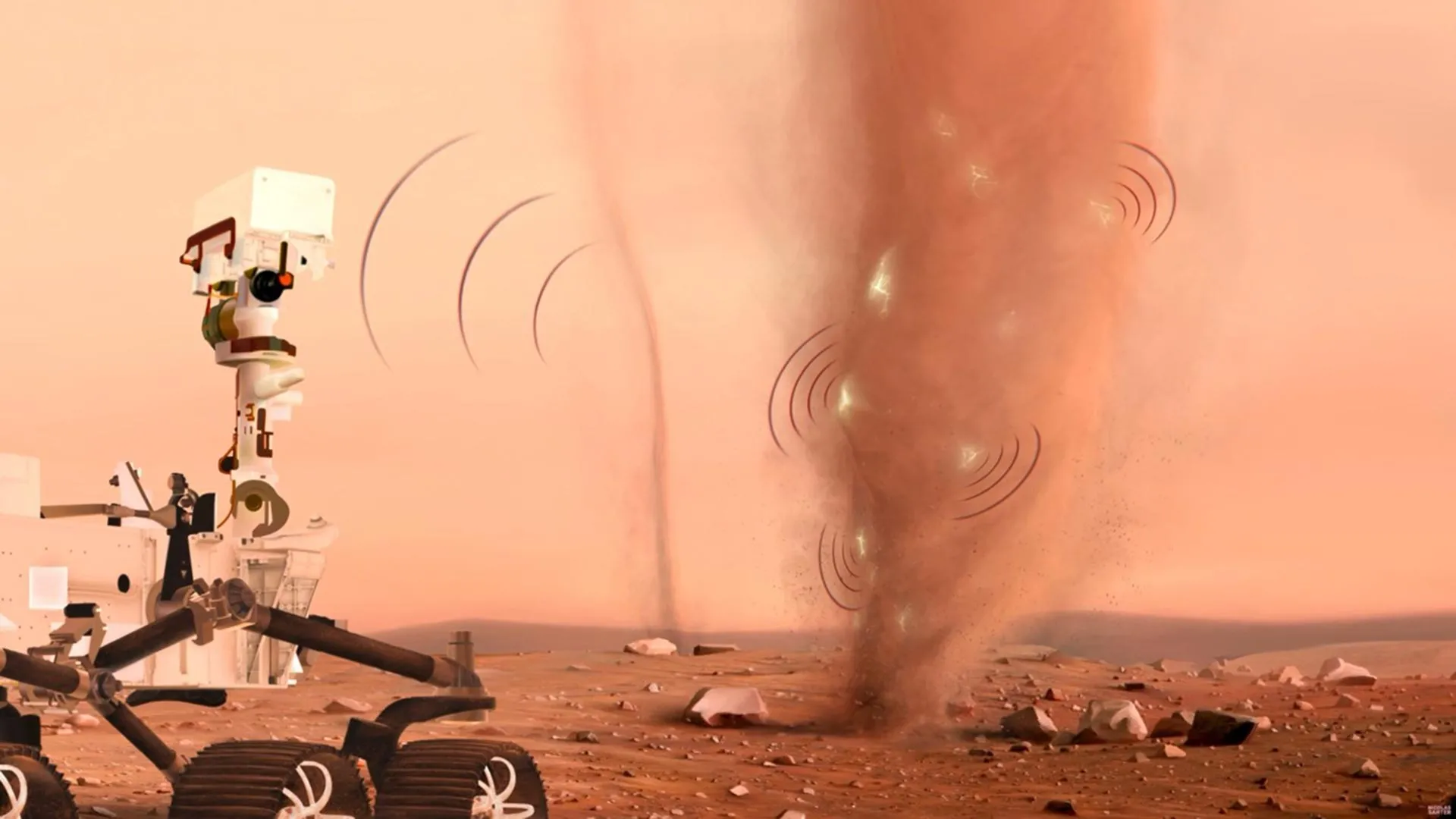

Mars dust storms are not just a visual spectacle; they are crackling with electricity. According to research published on December 29, 2025, scientists have discovered that dust devils on Mars can generate tiny electric sparks. This phenomenon, captured for the first time by the microphone on NASA’s Perseverance rover, has significant implications for our understanding of the Martian atmosphere and its chemistry.
The SuperCam instrument aboard Perseverance picked up unusual signals while studying two dust storms. This microphone, the first ever used on Mars, detected sounds originating from the center of these swirling dust devils. Researchers from the Institut de recherche en astrophysique et planétologie and other institutions analyzed these recordings, identifying them as both electromagnetic and acoustic signals produced by electric discharges.
These discharges resemble the mild static shocks experienced on Earth after touching a metal object in dry conditions. While scientists had long predicted the existence of such activity on Mars, this marks the first direct observation of electrical discharges in the planet’s atmosphere.
Understanding the Mechanism Behind Electric Sparks
The sparks are generated when numerous tiny dust grains collide and rub against one another. This friction causes the particles to accumulate electrical charges, which are released as short electric arcs just a few centimeters long. These bursts of electricity also create small shock waves, which can be detected audibly.
On Earth, dust particles can build up electric charges, particularly in arid regions. However, this process rarely leads to visible or measurable discharges. Mars presents a more conducive environment, as its thin atmosphere is primarily composed of carbon dioxide, requiring far less electrical charge to trigger sparks compared to Earth.
Implications for Mars’ Atmospheric Chemistry
The discovery of these electric discharges has important ramifications for how scientists view the chemistry of Mars’ atmosphere. The presence of electrical activity suggests that the atmosphere can reach charge levels sufficient to accelerate the formation of highly oxidizing compounds. These reactive substances could break down organic molecules on the Martian surface and alter various atmospheric chemicals.
One particularly intriguing aspect of this research pertains to the rapid disappearance of methane on Mars. Despite repeated detections, methane vanishes more quickly than existing models can account for. The electrically driven chemical reactions may play a role in its accelerated degradation.
The effects of electrical charging within dust storms could also influence the movement of dust across the Martian surface. Dust is crucial in shaping Martian weather and climate, and understanding these phenomena is key to grasping atmospheric behavior that remains largely unexplored.
Furthermore, the presence of electrical discharges raises practical concerns for future missions. Such discharges could interfere with the sensitive electronics aboard robotic spacecraft, posing risks for upcoming human exploration endeavors if not appropriately managed.
The SuperCam microphone has been operational since Perseverance’s landing in February 2021, capturing over 30 hours of audio from Mars. This includes not only wind gusts and sounds from the Ingenuity helicopter but now also the intriguing sounds linked to electric discharges in dust storms.
This groundbreaking research underscores the potential of sound recordings to reveal hidden processes on other worlds. By listening closely to the Martian atmosphere, scientists are uncovering phenomena that would otherwise remain undetected, broadening our understanding of this fascinating planet.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
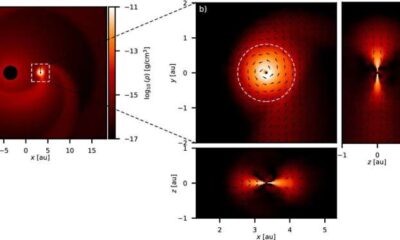
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws









