Health
Study Reveals Six Superfoods Can Rewind Biological Age by Over Two Years

Research published in the journal Aging suggests that significant dietary changes can lead to a remarkable reduction in biological age. In an eight-week randomized controlled trial, male participants aged between 50 and 72 who adopted a diet rich in methylated adaptogens experienced a decrease in their epigenetic age by an average of 2.04 years. In contrast, the control group, which did not modify their diet, saw an increase in biological age averaging 1.10 years.
The study highlights the potential of specific foods to influence aging markers. Participants in the experimental group incorporated six superfoods known for their high content of methylated adaptogens into their daily meals. This dietary shift appears to have provided a biological advantage, creating a difference of 3.14 years in epigenetic age when compared to the control group.
Researchers emphasized that the findings remained robust even after adjusting for factors such as weight changes and baseline epigenetic ages. This indicates a direct relationship between the consumption of these nutrient-rich foods and the reduction of aging indicators.
Understanding Methylated Adaptogens
Methylated adaptogens are compounds that support the body’s ability to adapt to stress and promote overall health. Foods rich in these compounds may play a crucial role in regulating biological processes associated with aging. While the exact mechanisms are still being studied, the results from this trial offer promising insights into how dietary interventions could contribute to healthier aging.
The implications of this research extend beyond just the participants. As populations worldwide continue to age, strategies that can effectively mitigate the effects of aging are of significant interest to health professionals and the general public alike.
The study’s findings emphasize the importance of nutrition in longevity. Incorporating the identified superfoods into one’s diet could potentially offer a natural approach to improving health outcomes as individuals age.
As the quest for effective anti-aging strategies continues, this research provides a foundation for further exploration into how dietary factors can influence biological age. Future studies may aim to explore the long-term effects of such diets and their impact on broader populations.
The journey toward healthier aging may lie in the foods we choose to consume, and this research underscores the potential for dietary changes to enact profound biological benefits.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
 Science1 month ago
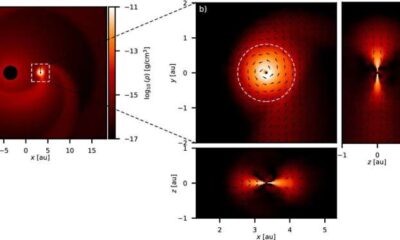
Science1 month agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws









