Politics
Review Study Advances Understanding of Historical Structure Materials
The preservation of historical structures is vital for maintaining connections to humanity’s artistic and architectural heritage. A new review study has been published, highlighting the importance of understanding the properties of building materials used in these structures. Conducted by a research team from the Department of Civil Engineering at Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University in Türkiye, this study, titled “Materials Characterization of Historical Structures: A Review,” aims to address gaps in the current methods used for material characterization.
This comprehensive review evaluates various analytical techniques for characterizing historical building materials, including natural stones like limestone and granite, as well as various types of mortars. The research aims to synthesize existing findings while clarifying the strengths and limitations of each characterization method. The findings are intended to guide researchers in selecting appropriate methodologies for their work.
Core Analytical Techniques Evaluated
The study systematically reviews key aspects of material characterization, focusing on four core categories of techniques.
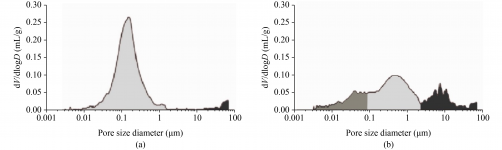
Physical and thermal property analysis methods include Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP), which assesses porosity and pore structure. For instance, MIP has identified two main pore size distributions in mortars from Amaiur Castle. Additionally, Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) evaluate thermal resistance, revealing that calcite decomposes between 600 °C and 900 °C, with a mass loss of 20% to 40% due to carbon dioxide emissions.
Chemical property analysis employs various techniques, such as X-ray Diffraction (XRD) to determine mineral compositions, including calcite and quartz prevalent in many mortars. Other methods, like X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), help quantify elemental and component analysis, providing insights into the materials’ foundational chemistry.
The study also assesses mechanical property analysis through non-destructive methods, including Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV), which correlates wave speed with the quality of concrete. Other methods, such as the Schmidt hammer and Flat-jack tests, measure surface hardness and in-situ stress, respectively, allowing for evaluations without damaging the historical structures.
Finally, visualization techniques like Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) provide detailed microstructural analysis. Infrared Thermography (IRT) is particularly useful for detecting moisture and hidden cracks, demonstrating its effectiveness in identifying invisible defects in structures like the Malatya Taşhoran Church.
Implications for Future Research and Conservation
The review references extensive studies on benchmarks, including Roman-period structures in Portugal and 11th to 14th-century buildings in Spain. These case studies validate the effectiveness of the reviewed techniques, confirming that a combined approach yields more reliable results.
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest. By providing a data-driven foundation for scientific inquiry, the findings aim to reduce costs in engineering and architectural analyses of historical structures. Furthermore, they support the development of restoration projects grounded in scientific understanding, ensuring that these cultural treasures can be preserved for future generations.
The paper, authored by Mertcan Demirel, Alican Topsakal, and Muhammet Gökhan Altun (corresponding author), represents a significant step forward in the field of cultural heritage preservation. For those interested in exploring the full text, it is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-025-1222-3.
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoIndonesia Suspends 27,000 Bank Accounts in Online Gambling Crackdown
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoHoneywell Predicts Record Demand for Business Jets Over Next Decade
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoMel Kiper Jr. Reveals Top 25 Prospects for 2026 NFL Draft
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach








