Science
NASA Reveals Timeline for Earth’s End: Life Could Last Billions More Years

NASA researchers, in collaboration with Toho University in Japan, have employed advanced supercomputers to model the future of life on Earth. Their findings suggest that while life as we know it will persist for billions of years, the potential end for human existence could arrive much sooner than previously anticipated.
Long-Term Projections for Life on Earth
The study indicates that the ultimate fate of all life on Earth is intimately tied to the sun’s lifespan. According to the researchers, the sun will continue to grow and heat up the planet, making conditions increasingly inhospitable. They estimate that all life could become impossible by the year 1,000,002,021, when extreme surface conditions will eliminate even the most resilient organisms.
While this date is millennia away, the outlook for humanity is more urgent. As the sun’s intensity increases, the Earth’s atmosphere will undergo significant changes. These alterations are expected to result in decreased oxygen levels, poor air quality, and rising temperatures. The researchers utilized a detailed model to predict these climate shifts, which are already observable today.
Current Signs and Future Implications
Recent phenomena, such as intensified coronal mass ejections and solar storms, are affecting the Earth’s magnetic field and potentially reducing atmospheric oxygen content. These developments provide researchers with valuable insights into the long-term effects of solar activity on our planet.
Moreover, human-induced climate change is accelerating the timeline for potential environmental collapse. Rising global temperatures and melting polar ice caps are already impacting ecosystems worldwide. While no specific end date for human life was established, the possibility of facing insurmountable environmental challenges well before the billion-year mark is a pressing concern for scientists.
Despite the lengthy timeline, researchers emphasize the need for proactive measures to ensure humanity’s survival. They advocate for technological interventions that could include closed life support systems and artificial habitats, designed to maintain livable conditions for as long as possible.
Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring other planetary bodies for potential colonization. NASA and SpaceX are investigating long-term missions to Mars as part of a broader strategy to sustain human life beyond Earth. These initiatives could play a critical role in securing the future of humanity as our home planet becomes increasingly uninhabitable.
The findings of this study underscore the importance of preparation and adaptation in the face of impending environmental changes. While the end of life on Earth is not imminent, understanding the long-term implications of our sun’s lifecycle and human impact on climate can guide future efforts and policies aimed at preserving life.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
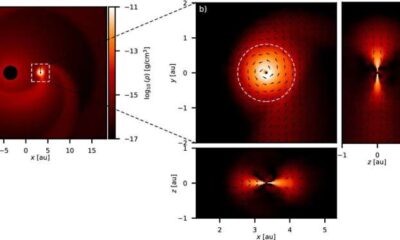
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws









