Science
Researchers Unveil New Model for Microbubble Behavior in Ultrasound
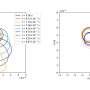
Recent advancements in biomedical technology have led to the development of a new model that analyzes the behavior of encapsulated microbubbles (EMBs) in viscoelastic fluids when subjected to ultrasound forces. These tiny gas-filled bubbles, surrounded by lipid or protein shells, are increasingly recognized for their significant potential in enhancing medical imaging and facilitating drug delivery.
Understanding how EMBs respond to ultrasound waves is crucial for optimizing their use in medical applications. When exposed to ultrasound, these microbubbles contract and oscillate, which can improve image contrast in ultrasound imaging and assist in drug delivery by creating pores in cell membranes through a process known as sonoporation. This dual functionality positions EMBs as promising tools in the fields of diagnostics and therapeutics.
Complex Behavior of Microbubbles
Despite their potential, the behavior of EMBs is notably complex. Recent studies have revealed that their performance can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the properties of the surrounding fluid and the frequency of the ultrasound waves. This complexity necessitates a deeper understanding of the mechanics involved to fully harness their capabilities in clinical settings.
The new model developed by researchers provides a more detailed insight into these dynamics. Utilizing advanced simulations, the model captures the intricate interactions between the microbubbles and the viscoelastic fluid environment. By replicating real-world conditions, the research aims to shed light on the factors that influence the oscillation patterns of EMBs, which are critical for optimizing their effectiveness in medical procedures.
The findings highlight that the viscoelastic properties of the surrounding fluid can significantly impact the stability and behavior of the microbubbles. For instance, variations in fluid viscosity can alter the oscillation frequency and amplitude of the bubbles, potentially affecting their ability to enhance imaging or deliver drugs efficiently.
Implications for Biomedical Applications
The implications of this research are substantial. As biomedical ultrasound technology continues to evolve, understanding the precise behavior of EMBs could lead to improved techniques for both imaging and therapeutic applications. Enhanced imaging contrast can facilitate earlier diagnosis of diseases, while more effective drug delivery systems could revolutionize treatment protocols for various conditions.
In summary, the exploration of microbubble behavior under ultrasound forces represents a significant step forward in the biomedical field. As researchers continue to refine these models, the potential applications of EMBs in medicine are likely to expand, opening new avenues for innovation in patient care and treatment methodologies.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
 Science2 months ago
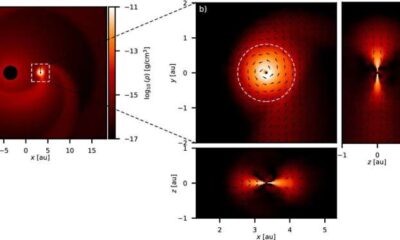
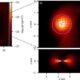
Science2 months agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws









