Science
Scientists Uncover Role of Water in Polymer Collapse Dynamics

Researchers have made significant strides in understanding the interactions between large molecules and water, particularly focusing on the behavior of the polymer Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), commonly known as PNIPAM. The international team successfully developed a method to observe these interactions in real time, revealing how water plays a critical role in the collapse of this polymer.
The study, published in Nature Communications, highlights the complex relationship between polymers and water. PNIPAM is a temperature-sensitive polymer that can switch between a hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) state. This property makes it a popular choice for various applications, including drug delivery systems and tissue engineering.
Innovative Techniques to Hear Molecular Interactions
To decipher the dynamics of water’s influence on PNIPAM, the research team utilized innovative acoustic methods. Instead of relying solely on visual techniques, they employed sound waves to detect changes in the polymer’s structure as it interacted with water. This approach allowed them to “hear” the molecular interactions, providing insights that traditional imaging techniques might miss.
According to the lead researcher from the University of California, Santa Barbara, the ability to monitor these interactions provides a deeper understanding of how water affects polymer behavior. “The collapse of PNIPAM under varying conditions is not just a visual phenomenon; it has audible aspects that can reveal much about the underlying mechanics,” they stated.
The study confirms that water bridges, microscopic structures formed when water molecules interact with the polymer, play a pivotal role in this process. As temperature changes, these water bridges influence the polymer’s collapse, leading to significant alterations in its physical properties.
Implications for Future Polymer Research
This groundbreaking research has broader implications for the field of polymer science. Understanding the collapse mechanisms of PNIPAM could lead to advancements in designing more effective materials for medical applications. For instance, tailoring the collapse properties of PNIPAM could enhance the efficiency of drug delivery systems, allowing for targeted therapies that respond to specific physiological conditions.
Moreover, the findings could pave the way for new materials in various industries, including textiles and coatings, where temperature sensitivity and responsiveness are crucial.
The international collaboration behind this study not only sheds light on fundamental scientific principles but also represents a step forward in the quest to harness the unique properties of polymers. As researchers continue to explore the intricate dance between water and polymers, the potential for innovative applications seems boundless.
This research underscores the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in science, blending physics, chemistry, and engineering to unlock new possibilities. The team’s work serves as a reminder that sometimes, listening closely can reveal the most profound insights into the natural world.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Science3 months ago
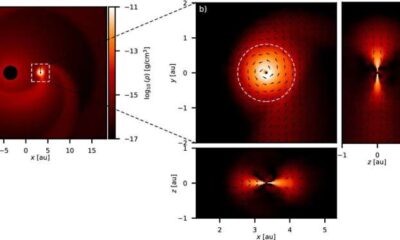
Science3 months agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-
 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months ago$2.2 Million Boost for Cancer Research and Training in Hawaiʻi
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoSacituzumab Govitecan Shows Promise for HR+/HER2− Breast Cancer
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoInterstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS Approaches Sun, No Threat to Earth
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies