Science
Africa’s Forests Shift from Carbon Sink to Carbon Source

A recent study reveals alarming changes in Africa’s forests, which have transitioned from being crucial carbon sinks to significant carbon sources. This transformation poses serious implications for global climate change efforts and biodiversity across the continent.
Research conducted by the University of Science and Technology and published in January 2024 highlights that Africa’s forests, once essential in absorbing carbon dioxide, now contribute to increased carbon emissions. The findings underscore the urgent need for reevaluation of conservation strategies in the region.
The study indicates that over the past decade, various factors have led to this shift. Deforestation, driven by agricultural expansion and urban development, along with climate-related stresses, has weakened the ability of these forests to sequester carbon effectively. As a result, emissions from these ecosystems are now higher than the carbon they absorb.
Key Findings on Carbon Emissions
The researchers found that Africa’s forests emitted approximately 1.2 billion metric tons of carbon in 2022, surpassing their carbon absorption capacity. This statistic starkly illustrates the environmental crisis that is unfolding. The shift is particularly concerning as forests play a critical role in regulating global temperatures and maintaining ecological balance.
Moreover, the study emphasizes that the loss of forest cover not only contributes to increased carbon emissions but also threatens biodiversity. Species that rely on these forests for habitat risk extinction due to habitat loss and changing environmental conditions.
Dr. Sarah Kambule, the lead researcher, stated, “The implications of this research are profound. If we do not act quickly to address the threats facing Africa’s forests, we risk not only worsening climate change but also losing invaluable biodiversity.”
Implications for Climate Change Strategies
The findings call for a reassessment of international climate strategies focused on forest conservation. With Africa being home to some of the world’s largest tropical forests, the continent’s shift to carbon emissions could hinder global efforts to limit temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement.
Policymakers and environmental organizations are urged to prioritize sustainable land management practices. These practices can help restore forest areas and improve their resilience to climate change. Initiatives aimed at reforestation and afforestation, along with stricter regulations on land use, are critical in reversing this trend.
The report serves as a wake-up call, highlighting that the health of Africa’s forests is intrinsically linked to global climate stability. As nations grapple with the impacts of climate change, it is essential to recognize the vital role that forests play in achieving sustainability goals.
In conclusion, the transition of Africa’s forests from carbon sinks to carbon sources is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. As the research indicates, without decisive action, the consequences for both the environment and global efforts to combat climate change could be catastrophic.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-
 Science2 weeks ago
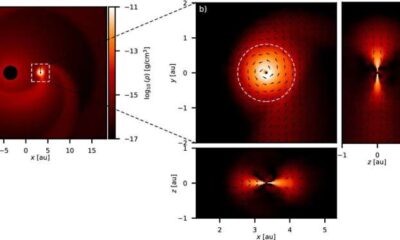
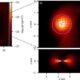
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoTruist Financial Increases Stake in Global X Variable Rate ETF