Science
Breakthrough Coating Technology Triples Lifespan of Brain Electrodes
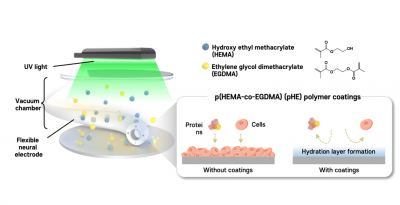
A research team from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has developed an innovative coating technology that significantly extends the lifespan of implanted electrodes used for recording brain signals. This advancement, led by Dr. Hyejeong Seong at the Brain Convergence Research Division, increases the duration of effective signal recording from one month to over three months. Collaborating with Prof. Seongjun Park from Seoul National University, the researchers aim to enhance the efficacy of brain-computer interfaces and neural prosthetics.
The study highlights the critical need for longer-lasting electrodes in the field of neuroscience. Current technologies often face challenges due to the body’s inflammatory response, which can degrade electrode performance over time. The new coating developed by the KIST team mitigates this issue, providing a more stable environment for neural interfacing. This breakthrough is expected to facilitate more reliable long-term monitoring and treatment of neurological conditions.
Researchers conducted extensive tests to evaluate the performance of the new coating. The results demonstrated a clear improvement in electrode durability, with the lifespan extending beyond the previously established limits. This development could pave the way for more advanced applications in neurotechnology, including rehabilitation devices and clinical research tools.
Sang-Rok Oh, President of KIST, expressed optimism about the implications of this research. “The enhanced longevity of implanted electrodes is a significant step forward in making brain signal recording more effective and sustainable,” he stated. The work aligns with ongoing efforts to improve patient outcomes through technological advancements in medical science.
As the research progresses, the team plans to explore further enhancements to their coating technology. Their goal is to create an even more robust solution capable of supporting long-term neural interfaces. This innovation is expected to have a profound impact on the treatment of various neurological disorders, offering new possibilities for patients and healthcare providers.
The findings of this study contribute to the broader field of neurotechnology, which is rapidly evolving as researchers seek to bridge the gap between human cognition and machine interaction. With continued investment and research, technologies like these could revolutionize how we approach brain health and cognitive function.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
 Science1 month ago
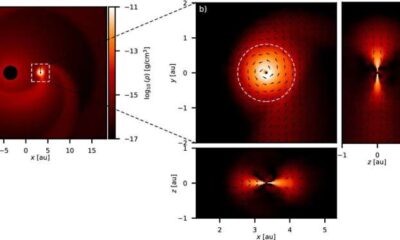
Science1 month agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach








