Health
Understanding High Triglycerides: Key to Heart Health

High triglyceride levels can significantly impact heart health, raising concerns among healthcare professionals. According to the American Heart Association, triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood, and elevated levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Understanding the implications of high triglycerides is essential for maintaining overall heart health. These fats are produced when the body converts excess calories into energy and can be influenced by diet, lifestyle, and genetic factors. The association between triglycerides and other lipids, such as low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL), plays a crucial role in assessing heart health.
What Are Triglycerides and Why Do They Matter?
Triglycerides serve as a primary energy source for the body, but when levels rise above 150 milligrams per deciliter, they can pose health risks. The American Heart Association classifies triglyceride levels as follows: normal (less than 150 mg/dL), borderline high (150-199 mg/dL), high (200-499 mg/dL), and very high (500 mg/dL or more).
High triglyceride levels often accompany other conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, which can further increase the risk of heart disease. When triglycerides are elevated, they may contribute to the hardening of arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, which can result in heart attacks or strokes.
Recent studies indicate that high triglycerides can have a more significant impact on heart health than previously thought. A report published in May 2023 highlights that individuals with elevated triglycerides, even with normal cholesterol levels, are at an increased risk of cardiovascular events. This finding emphasizes the need for comprehensive lipid profiling and management in patients.
Managing Triglyceride Levels for Better Heart Health
Diet and lifestyle changes can effectively lower triglyceride levels. The American Heart Association recommends a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing sugar and refined carbohydrates, along with increasing physical activity, can also contribute to improved triglyceride levels.
In some cases, medications may be necessary to manage high triglycerides. Statins, fibrates, and omega-3 fatty acids are common treatments prescribed by healthcare providers. Regular monitoring of lipid levels is crucial for those at risk, enabling timely interventions to prevent serious health complications.
Understanding the role of triglycerides in heart health is essential for individuals and healthcare providers alike. By prioritizing awareness and proactive management, it is possible to reduce the risk of heart disease and promote long-term cardiovascular health.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
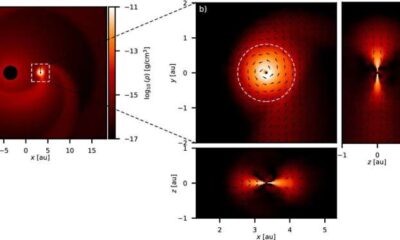
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws









