Science
Researchers Explore Evolutionary Roots of Consciousness in Birds
Recent research from Ruhr University Bochum delves into the evolutionary mechanisms that led to the development of consciousness in some species while others remain non-conscious. The findings, published in two articles, aim to shed light on the adaptive advantages of consciousness and how observing avian behavior may provide insights into this complex phenomenon.
The researchers, led by a team of biologists, examined various species to understand why certain organisms have evolved consciousness. They specifically focused on birds, which exhibit a range of cognitive abilities. This investigation not only aims to clarify the evolutionary significance of consciousness but also explores the implications for understanding intelligence in non-human species.
Understanding Consciousness Through Avian Studies
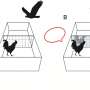
Birds, particularly species like crows and parrots, display remarkable problem-solving skills and social behaviors that suggest higher cognitive functions. The studies published in January 2024 reveal that these traits may be linked to their evolutionary history. By analyzing the behaviors and brain structures of different bird species, the researchers found that certain environmental pressures may have driven the development of consciousness.
One of the key findings highlights how the ability to process complex social interactions may confer significant advantages in survival and reproduction. For instance, birds that can recognize individual members of their social groups tend to form stronger bonds and cooperate more effectively, leading to improved foraging success and predator avoidance. Such insights support the idea that consciousness serves a vital role in navigating social dynamics within species.
Additionally, the research highlights the concept of “cognitive convergence,” where unrelated species develop similar cognitive traits in response to similar environmental challenges. This phenomenon can be observed in birds and primates, both of which have evolved sophisticated cognitive abilities despite their divergent evolutionary paths.
Implications for Understanding Human Consciousness
The implications of this research extend beyond avian studies. By examining the cognitive abilities of birds, scientists gain valuable perspectives on the evolutionary origins of consciousness in humans. Understanding how other species developed advanced cognitive functions can inform theories on human consciousness and offer insights into our own evolutionary history.
The studies challenge the notion that consciousness is a unique trait of humans and suggest that it may be more widespread among various species. This perspective encourages a reevaluation of how we understand intelligence and consciousness across the animal kingdom.
The ongoing research at Ruhr University Bochum contributes to the broader discourse on consciousness, inviting further exploration into the evolutionary pathways that have shaped cognitive abilities in different species. As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of consciousness, the findings from avian studies could significantly reshape our understanding of intelligence and awareness in both humans and animals.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-
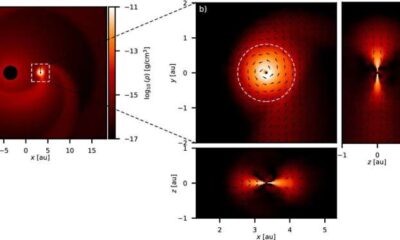
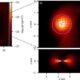 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoTruist Financial Increases Stake in Global X Variable Rate ETF