Science
Researchers Identify Key Factors in Hydrogen Isotope Exchange
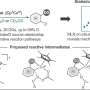
A recent study led by Professor Mónica H. Pérez-Temprano from the Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ) and Professor Anat Milo from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has unveiled critical insights into how specific substrate characteristics influence hydrogen isotope exchange pathways. This research focuses on C–H deuteration reactions, a process essential in various fields, including organic chemistry and materials science.
The collaborative effort between the two research teams highlights the importance of reaction conditions tailored to the substrate’s properties. The study reveals that the nature of the substrate can dictate the necessary reaction conditions, which ultimately determine the efficiency and outcome of the deuteration reaction.
Understanding the Mechanisms
The findings indicate that certain substrates require specific environmental conditions to facilitate the desired chemical transformations. This understanding opens new avenues for optimizing C–H deuteration reactions, which are pivotal in synthesizing complex molecules. The research methodically examined various substrates under controlled conditions, providing a comprehensive analysis of how these factors influence reaction pathways.
C–H deuteration reactions are integral in producing isotopically labeled compounds, which are crucial for a range of applications, including drug development and chemical tracing studies. The team’s research not only enhances the fundamental understanding of these reactions but also suggests practical implications for improving reaction yields and selectivity.
The collaboration underscores the significance of interdisciplinary approaches in tackling complex scientific challenges. By combining expertise from different fields, the researchers were able to explore new dimensions of chemical reactivity and substrate interaction.
Professor Pérez-Temprano noted, “Our work demonstrates how the substrate’s features can direct the course of chemical reactions, leading to more efficient synthetic routes.” This statement highlights the potential impact of their research on future chemical processes.
Future Implications and Applications
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest. As industries increasingly seek more efficient and sustainable methods for producing chemicals, this work provides a framework for developing new strategies in synthetic chemistry. The ability to control reaction pathways based on substrate characteristics could streamline processes in pharmaceuticals and materials engineering.
In conclusion, the collaborative research between the Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia and Ben-Gurion University sets a precedent for future studies in chemical reactivity. By emphasizing the role of substrates in determining reaction conditions, this work not only contributes to theoretical knowledge but also paves the way for practical advancements in chemical synthesis. The study was published recently and is expected to influence ongoing research in this vital area of chemistry.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-
 Science2 weeks ago
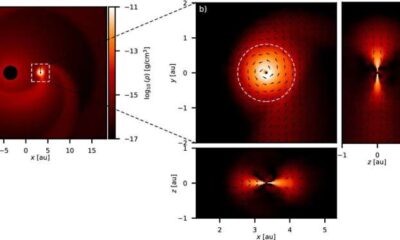
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoTruist Financial Increases Stake in Global X Variable Rate ETF