Health
Researchers Uncover Mechanism to Clear Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer’s
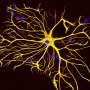
A team of researchers at Baylor College of Medicine has identified a natural mechanism that effectively removes amyloid plaques from the brains of mouse models suffering from Alzheimer’s disease. This groundbreaking discovery may pave the way for new treatments aimed at preserving cognitive function in individuals affected by this debilitating condition.
The study highlights the role of astrocytes, which are star-shaped brain cells. These cells are crucial for maintaining brain health and have now been found to actively participate in clearing the toxic amyloid plaques that accumulate in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. By harnessing this natural process, scientists hope to develop therapeutic strategies that can replicate this mechanism in humans.
Mechanism Behind Amyloid Plaque Clearance
The research reveals that astrocytes respond to the presence of amyloid plaques by mobilizing to the affected areas of the brain. Once there, these cells engage in a cleanup process, effectively removing the toxic substances that contribute to cognitive decline. This process not only reduces the burden of amyloid plaques but also appears to preserve cognitive function in the mouse models used in the study.
Dr. Paul A. Janik, one of the leading researchers in the study, emphasized the significance of these findings. “Our research shows that astrocytes can be recruited to clear amyloid plaques, presenting a promising avenue for future Alzheimer’s therapies,” he stated. The study provides a deeper understanding of the brain’s intrinsic repair mechanisms and the potential to exploit them in combating Alzheimer’s disease.
The research team’s findings were published in a recent issue of a prestigious scientific journal. The implications of this study could be transformative, as current Alzheimer’s treatments primarily focus on symptoms rather than addressing the underlying causes. By targeting amyloid plaques, a hallmark of the disease, new therapies could significantly alter the course of Alzheimer’s for millions worldwide.
Future Directions for Alzheimer’s Research
This discovery opens avenues for further research into enhancing the function of astrocytes or directly stimulating their activity in the presence of amyloid plaques. With approximately 50 million people globally living with dementia, the urgency for effective treatments has never been greater.
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine are optimistic that their findings will lead to clinical trials in the near future. The potential to improve cognitive function and quality of life for those affected by Alzheimer’s disease could represent a significant breakthrough in neurology.
As the scientific community continues to explore the role of astrocytes in brain health, this study serves as a crucial step towards understanding and ultimately combating Alzheimer’s disease.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-
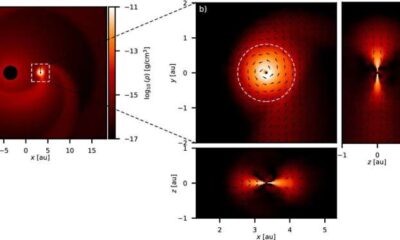
 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoTruist Financial Increases Stake in Global X Variable Rate ETF








