Health
Study Finds High-Intensity Training Enhances Muscle Function

A recent study from the renowned Karolinska Institutet, published in the journal eBioMedicine, indicates that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) significantly improves muscle function in individuals recently diagnosed with inflammatory muscle disease. This finding challenges the effectiveness of traditional home exercise programs, suggesting a more dynamic approach to rehabilitation.
The research focused on the impact of HIIT on muscle endurance and overall fitness in patients suffering from this debilitating condition. Inflammatory muscle disease can cause severe weakness and fatigue, making effective exercise programs crucial for patient recovery and quality of life.
Participants in the study engaged in a structured HIIT regimen, which involved short bursts of intense exercise followed by rest or low-intensity activity. This method proved to be more beneficial than conventional exercise routines, which typically emphasize steady-state activities.
The study’s lead author, Dr. Anna Johansson, a researcher at Karolinska Institutet, emphasized the importance of tailored exercise interventions. “Our research demonstrates that incorporating high-intensity training into rehabilitation programs can yield substantial benefits in muscle function for patients with inflammatory muscle disease,” she stated.
Over the course of the study, subjects who underwent HIIT showed measurable improvements in both muscle strength and endurance compared to their counterparts participating in traditional exercise. The results highlight the potential for HIIT not just to enhance physical capabilities but also to improve overall well-being in patients facing chronic muscle conditions.
Significance of the Findings
The implications of this research extend beyond individual patient outcomes. By establishing HIIT as a superior option for improving muscle function, healthcare providers may need to reconsider rehabilitation strategies for patients with inflammatory muscle disease. Traditional exercise programs, while beneficial, may not provide the same level of improvement in muscle endurance and fitness.
As these findings gain attention, there is a growing interest in further studies to explore the long-term effects of high-intensity training in various patient populations. The objective is to refine protocols that maximize rehabilitation benefits for those affected by inflammatory muscle disease.
In conclusion, the study from Karolinska Institutet opens new avenues for rehabilitation practices, emphasizing the role of high-intensity interval training in improving muscle function for individuals battling inflammatory muscle disease. With further research and implementation, HIIT could become a standard recommendation in therapeutic exercise regimens, transforming the recovery experience for many patients.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-
 Science2 weeks ago
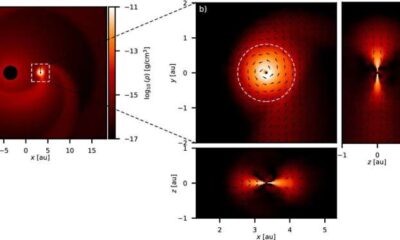
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoMel Kiper Jr. Reveals Top 25 Prospects for 2026 NFL Draft