Science
New Solar-Powered System Cleans Antibiotics from Soil
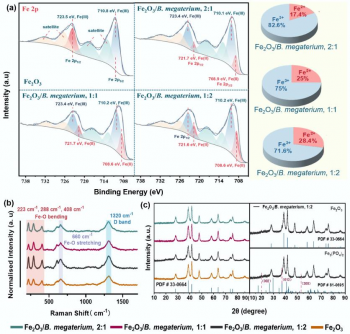
Researchers have developed an innovative approach to environmental cleanup that harnesses solar energy to degrade harmful pollutants, particularly antibiotics. A study published on September 15, 2025, in the journal Environmental and Biogeochemical Processes, reveals that the interaction between iron minerals and the bacterium Bacillus megaterium can significantly enhance the degradation of antibiotics like tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) and chloramphenicol (CPL).
This breakthrough is a significant advancement in bioremediation techniques, highlighting the ability of non-phototrophic microorganisms to utilize solar energy through mineral-microbe interactions. Traditionally, solar energy has been recognized mainly for its role in photosynthesis, but recent findings indicate its broader influence on microbial metabolism and geochemical processes, even in environments where light penetration is limited, such as saturated soils and sediments.
The study, led by researchers from Kunming University of Science and Technology and the University of Massachusetts, investigates the co-culturing system of iron minerals, specifically Fe2O3 (iron oxide) or FeOOH (iron hydroxide), with B. megaterium. The researchers explored the mechanisms of electron accumulation and release during light-dark cycles. The system demonstrated a continuous charge-discharge function, exhibiting a phenomenon described as “photovoltaic memory.”
During the experiments, the electron storage capacity, measured as total accumulated charge (∑σ), increased with higher bacterial density. This indicates that denser biofilms are more efficient in capturing and storing energy. The charge accumulation during light exposure was significantly higher than the release in darkness, with values increasing from 2.87 μC·cm−2 to 4.08 μC·cm−2 over several cycles.
Remarkably, following just 60 minutes of light exposure, the degradation efficiency for TCH improved by 66.7% and for CPL by 46.7%. This enhanced degradation was attributed to the synergistic interactions between the iron minerals and the bacteria, which facilitated efficient electron transfer and storage, enabling the system to function akin to a “biological capacitor.”
The findings from this study suggest that the Fe2O3/B. megaterium biofilm system offers a promising, sustainable method for addressing environmental pollution, particularly in soil and groundwater. It leverages light-driven charge storage and release mechanisms, providing a viable solution for treating pollutants in dark environments without requiring continuous illumination.
This novel biocapacitor mechanism could transform current bioremediation practices, particularly for sites contaminated with antibiotics. The research indicates that this approach is not only cost-effective but also energy-efficient, potentially revolutionizing methods for cleaning up polluted environments.
The study received financial support from several organizations, including the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Key Research and Development Program of China. The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest, offering practical solutions for environmental cleanup in diverse ecosystems.
As the field of sustainable pollution control continues to evolve, the integration of solar energy into bioremediation represents a significant step forward in addressing the global challenge of antibiotic contamination in soils and groundwater.
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoIndonesia Suspends 27,000 Bank Accounts in Online Gambling Crackdown
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoHoneywell Predicts Record Demand for Business Jets Over Next Decade
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoMel Kiper Jr. Reveals Top 25 Prospects for 2026 NFL Draft
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoNew Jersey Voters Urged to Register Ahead of November Election
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025








