Science
Rare Earths and Electric Motors: Key Developments in 2025

The year 2025 witnessed significant developments in the fields of rare earth elements, magnets, and electric motors, with a particular focus on geopolitical implications and technological advancements. The resurgence of the Mountain Pass mine in California marked a key moment, as it began producing industrial quantities of rare-earth oxides, specifically neodymium and praseodymium. This mine, once responsible for up to 70 percent of the world’s rare earth supply, has been revitalized after years of decline, placing it back in the spotlight of global resource production.
China currently dominates the market for rare earth elements, controlling between 85 and 99 percent of global supply. This situation has left countries like the United States and its allies heavily reliant on Chinese production for critical materials essential for motors, semiconductors, and military systems. The Mountain Pass mine’s increased output is a pivotal development in the ongoing quest for supply chain independence from China, especially as these rare earth elements are vital for various technologies, including night-vision gear and advanced aircraft systems.
U.S. Strategies to Secure Rare Earth Supply Chains
Throughout 2025, the Trump administration actively sought to establish alternative rare-earth supply chains. The strategy involved negotiations with Ukraine regarding its rare-earth deposits, despite skepticism from mining experts about the viability of these resources due to ongoing conflict and inadequate processing technologies.
In a notable development, the U.S. Department of Defense announced a significant investment of $400 million in MP Materials, acquiring a 15 percent stake in the company. This investment set a price floor of $110 per kilogram for specific rare earth oxides, nearly double the current prices from Chinese suppliers. This move not only underscores the U.S. commitment to bolstering its domestic production capabilities but also highlights the strategic importance of rare earths in national security.
As the administration navigated its approach, there was a shift towards collaboration with allies like Australia and Canada, both rich in rare earth resources. Canada’s Neo Performance Materials operates a significant rare-earth-oxide refining plant in Estonia, which is among the few outside Asia capable of producing these essential materials.
Innovations in Magnet and Motor Technology
2025 was also marked by notable technological advancements in magnet and motor production within the United States. MP Materials began trial production of neodymium-iron-boron magnets at a facility in Texas, with plans to scale output to between 2,000 and 3,000 tonnes annually. A substantial agreement with Apple, worth $500 million, aims to supply these magnets for use in various devices, enhancing the domestic tech landscape.
In the realm of electric propulsion, researchers at Victoria University in New Zealand tested electric propulsion magnets based on magnetoplasmadynamic thrusters. This innovative approach leverages high-temperature superconducting tape to reduce power requirements, with a technology demonstration scheduled for operations on the International Space Station.
Another significant development comes from the startup Hinetics, which focuses on high-temperature superconducting motors for electric aircraft. This technology, backed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy, aims to achieve a specific power output of 40 kW/kg, surpassing current commercial motor standards.
Airbus is also in the race to develop electric propulsion systems, announcing plans for a zero-emission passenger airliner powered by fuel cells and superconducting motors. The ambitious project, named ZEROe, aims for commercialization in the 2040s, positioning Airbus ahead of competitors in sustainable aviation.
Additionally, Donut Lab introduced an innovative in-wheel hub motor, boasting a weight of just 40 kg and a power output of 650 kW, addressing long-standing challenges in electric vehicle design.
As 2025 drew to a close, the discussions surrounding Greenland’s rare earth resources continued, with the region being eyed for potential annexation due to its mineral wealth. The complexities of mining in this sparsely populated territory, however, present significant challenges that must be addressed.
The developments of 2025 underline the intricate relationship between rare earth materials and global technology, setting the stage for ongoing geopolitical and industrial shifts in the years to come.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNew Gel Offers Hope for Regrowing Tooth Enamel in Dentistry
-
 Science1 month ago
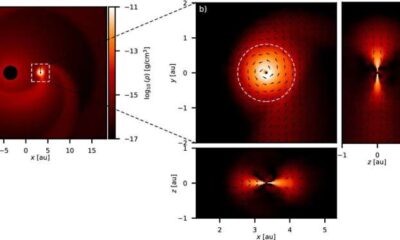
Science1 month agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoPark Jung Min’s Endearing Moment with Hwasa Steals Show at Awards
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoSampson County Celebrates Susie Faison’s 100th Birthday Milestone
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws