Business
U.S. Energy Grid Faces Risks from Weather and Data Demands

The energy infrastructure in the United States is under significant pressure as winter approaches, raising concerns over potential power outages caused by severe weather. Years of underinvestment and a lack of coordination among utilities have left the grid vulnerable. States such as Texas and California face recurring power outages during extreme weather events, which can include winter storms and heatwaves.
In February 2021, Storm Uri brought freezing temperatures to Texas, resulting in widespread power failures that affected millions. Many Texans were left without electricity, heat, or running water as critical infrastructure froze. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) reported that the state’s grid operator, ERCOT, implemented 20 gigawatts (GW) of rolling blackouts to avert a total system collapse, marking the event as the largest manually controlled load-shedding incident in U.S. history. Approximately 4.5 million people lost power for several days.
The U.S. energy grid’s fragmented structure complicates efforts to enhance its resilience. Different states manage their own sections of the grid, and numerous utilities oversee various infrastructure components. This disjointed system leads to disparities in investment and preparedness, with some regions benefiting from stronger infrastructure than others.
To address these issues, the Biden administration introduced the $2 trillion Bipartisan Infrastructure Law in 2021, which allocated $100 billion to modernize the electric grid. Despite these initiatives, challenges remain that hinder a comprehensive upgrade of the energy infrastructure, leaving it ill-equipped for severe weather.
As if this were not enough, the rapid expansion of data centres across the U.S. further exacerbates concerns about energy supply. Tech companies have heavily invested in these facilities to support advancements in technologies like artificial intelligence, significantly increasing energy demand. Texas, with its growing renewable energy capacity and abundant natural gas resources, has become a hotspot for new data centre projects, prompting fears about potential energy shortages during extreme cold.
In November, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) cautioned that the continuous energy demands of data centres could strain the electricity supply, particularly in cold weather conditions. The organization highlighted that power demand in Texas could spike to as much as 85.3 GW during severe winter storms. While the state’s total electricity capacity stands at 92.6 GW, this could drop to approximately 69.7 GW in extreme conditions, creating a deficit of over 15 GW.
NERC’s analysis indicated that the rapid growth in energy consumption from new data centres and other large industrial users is driving higher electricity demand forecasts, raising the risk of supply shortfalls. Although the grid is expected to remain stable during normal peak demand, the situation becomes precarious during severe winter events.
Over 120 GW of new projects have requested to connect to the Texas grid, a staggering 170 percent increase since January. Approximately 73 percent of these requests pertain to data centres, as reported by ERCOT. If all proposed data centres are constructed, they could consume power equivalent to the average annual usage of nearly 154 million homes.
Experts warn that while the potential for growth exists, the complete development of these projects is unlikely due to insufficient power resources. The ongoing underinvestment in the U.S. grid, coupled with the rising demand from data centres, poses a serious risk of power shortages during winter storms. This situation underscores the urgent need for stronger regulations to ensure the electricity supply is both reliable and robust enough to meet future demands.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Joins $25.6M AI Initiative for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoIROS 2025 to Showcase Cutting-Edge Robotics Innovations in China
-
 Science2 weeks ago
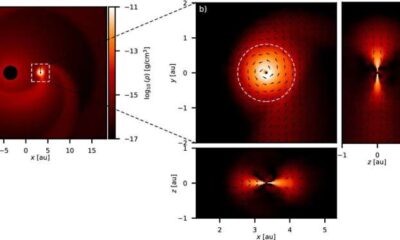
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Red Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoStone Island’s Logo Worn by Extremists Sparks Brand Dilemma
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoStartup Liberate Bio Secures $31 Million for Next-Gen Therapies
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBravo Company Veterans Honored with Bronze Medals After 56 Years
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoMary Morgan Jackson Crowned Little Miss National Peanut Festival 2025
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Considers Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoTop Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Radiant Skin in 2025
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoArizona State University Transforms Programming Education Approach
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYamamoto’s Mastery Leads Dodgers to 5-1 Victory in NLCS Game 2
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoMel Kiper Jr. Reveals Top 25 Prospects for 2026 NFL Draft









